Ubicación
Mexicali, BCN
Horarios
Lunes a Viernes: 8AM - 5PM
Sábado: 8AM - 2PM
Domingo: Cerrado

Accumulated amortization is recorded as a credit to the accumulated amortization account (a contra asset) and a debit to the amortization expense account. This reduces the asset’s book value and recognizes the expense on the income statement. Understanding these differences is crucial for accurate financial reporting and analysis. Typically, the accumulated amortization account is reflected on the balance sheet as a contra account (which offsets the balance in a related account) and is tied with the intangible assets line item.
This section will discuss how accumulated amortization applies to loans and the different aspects of loan amortization. After five years, the accumulated amortization totals $100,000, reducing the franchise agreement’s book value to $100,000. This accounting treatment ensures that the expense is matched to the revenues generated by the franchise. For example, a tech company with $50,000 in accumulated amortization for its software licenses reduces the asset’s original cost of $100,000 to a normal balance net book value of $50,000.

One important thing to note is that accumulated amortization is a contra asset account, which means that it has a credit balance. This is because it is subtracted from the original cost of the asset to arrive at its net bookkeeping for cleaning business book value. Typically, amortization is classified as a contra-asset account on the balance sheet. You can often find this information below the line for the unamortized intangible asset. Yet, companies often amortize one-time expenses, classifying them as capital expenses on the cash flow statement and paying off the cost over time.
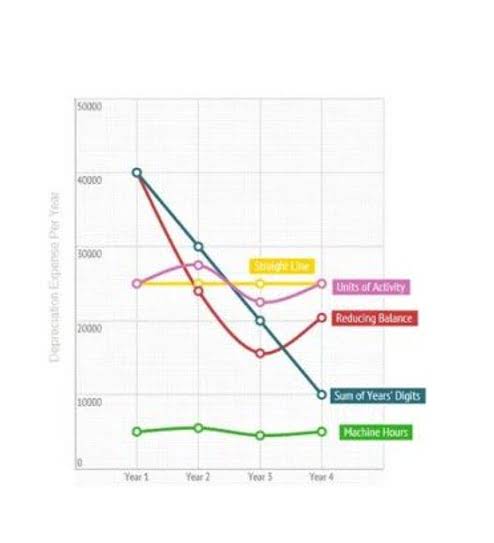
However, rather than being reported at its original cost indefinitely, the asset’s cost is gradually reduced over time through amortization. Unlike tangible assets, which can be depreciated over time, intangible assets are amortized. Depreciation is the allocation of the cost of tangible assets, such as buildings or equipment, whereas amortization applies to intangible assets. Amortization is an accounting method used to allocate the cost of an intangible asset over its useful life by gradually reducing its carrying value on the balance sheet.
On the income statement, typically within the “depreciation and amortization” line item, will be the amount of an amortization expense write-off. Depending on the type of asset — tangible versus intangible — there are differences in the calculation method allowed and how they are presented on financial statements. Tangible assets may have some value when the business no longer has a use for them. Depreciation is therefore calculated by subtracting the asset’s salvage value or resale value from its original cost. The depreciated accumulated amortization amount expensed each year is a tax deduction for the company until the useful life of the asset has expired.
